What Are Some Similarities In Restraining Small And Large Animals
Proper Animal Treatment & Restraint
Fundamentals of Patient Interaction
- Personnel should motility effectually and interact with the animal 25-50% slower than their natural inclination. A universal observation I have made in watching people handle animals is that they move too apace and pay too little attending to what the creature is telling them at any moment. Animals almost E'er warn before escalating assail or escape, especially dogs. The problem is that we tend to miss these warning signs.
- Doctors and staff should remain calm and neutral no thing how desperately the animal may comport. Poor beliefs should be ignored; however, whatsoever tendency toward improve beliefs—no matter how small—should be immediately rewarded in some style.
- In 98% of cases, injuries to humans occur because someone did something unwise, became complacent while working on the animal, or did not know how to read the animal'south body language. Think that beliefs is constantly irresolute. Just because the animal is friendly at the beginning of the exam or procedure, does non mean the fauna volition remain so 3 seconds later on. Always assume the animal may injure you at whatsoever fourth dimension – be cautious and prudent, but not paranoid. Always keep your body parts away from the animal's weapons.
- Restraint techniques should never involve any of the post-obit: concrete reprimands of any type (jerking on leashes, hitting or hitting the animal, biting the animal, etc.); pinning the animal'due south head or neck in doorjambs or nether your body; alpha rolls; scruff shaking; cuffing under the mentum; hanging with leashes or choking the animal in whatever way; or "pile-ups" (having several people grab concur of the brute and pin it to the footing or table).
- Avert scruffing cats as a routine restraint method. Scruffing alone is really non a secure way to restraint a cat, and it aggravates many cats more than necessary. Scruffing does non trigger some magical relaxation in cats. Cats exercise have a flexor reflex when picked up by the scruff when they are kittens, but there is no biological reward for an adult cat to get limp when grabbed by the back of the neck. Adult cats are only subjected to this activeness in four general contexts: fighting, play fighting, convenance and predatory attacks. Culling methods tin can be more successful.
Interpreting an Animal's Body Linguistic communication and Behavior
- Changes in the patient's environment may cause normal behavior patterns to alter
- Body language communicated by the creature tin demonstrate clearly how it feels toward other animals, people, and its surroundings
- Trunk linguistic communication tin can help you determine how piece of cake or hard an beast may be during handling and restraint
Patient Restraint Considerations
- Restraint is the procedure of; property dorsum, checking, or suppressing an activity and/or keeping something under control using prophylactic and some means of physical, chemical, or psychological action.
- Restraint is a necessary tool used past veterinary staff to allow an beast to be controlled for various procedures
- Safety of the patient and staff are paramount!
- Sedatives/Tranquilizers – are sometimes necessary to go on a patient calm or pain free during certain stressful procedures or circumstances.
 Why Proper Restraint Techniques?
Why Proper Restraint Techniques?
- Prevents injury
- Necessary for examinations and treatments
- More comfortable for animal and handler
- A First Aid Kit should exist bachelor for all bites and scratches
- All Fauna bites must be reported to the NY Dept. of Wellness
Planning the restraint procedure
- When preparing to restrain a patient, always brand certain the area has enough room, is clean, dry out, and well lit
- A plan should be discussed:
- Motion whatsoever plush equipment
- Nonslip area
- Temperature should be considered
- What should be washed if animal happens to get away from restrainer
- Support program (Plan B!)
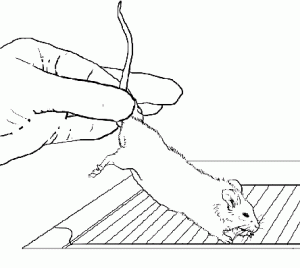 Rodents & Ferret Restraint & Handling
Rodents & Ferret Restraint & Handling
Mice
- Grasp the tail close to the body with one mitt
- Employ the other hand to grasp loose skin in the neck and shoulder surface area.
Larger Rodents and Ferrets
- Brand sure the fauna is awake to avoid bites
- Hold in one hand, loving cup other over its caput
- Wrap thumb and index

- finger around neck and under mentum
- Do not over tighten fingers effectually chest equally this can impair breathing
 Cats Restraint & Handling
Cats Restraint & Handling
- Cats tend to be 1 of the well-nigh hard during restraint when they become upset and aggressive from stress
- Safely restrain and have control over head
- True cat bags: control the limbs and head
- Squeeze cages: wire boxes with small slots that allow injections to be given
- To piece of work effectually head:
- Wrap or swaddle in a blanket or place in "cat bag"
- Allows handler to grasp and hold the back of the caput between the pollex and fingers
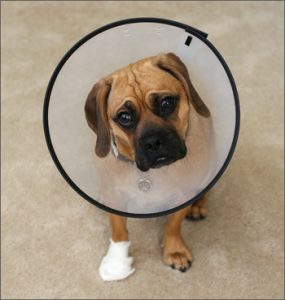 Making an E-collar – Cone of SHAME
Making an E-collar – Cone of SHAME
- Measure the pet'south cervix and the distance from his collar to the tip of his nose
- Mark these measurements on a piece of rigid paper-thin or plastic.
- Nosotros're going to utilise construction paper
- Make a V-shaped cut from the outer border to the inner circle.
- Punch holes along both edges of the collar.
- Lace a shoe cord or yarn through the holes to secure the collar around your pet'southward neck.
 Boosted Canine Techniques
Boosted Canine Techniques
- Rabies pole or snare pole should only be used when absolutely necessary.
- A rabies Pole has a noose on the terminate, and acts as a leash
- Captures and restrains dogs
- Pulling tin crusade severe head and cervix injuries
Handling Cats
When Attempting to Restrain I Should:
- Use the least amount restraint necessary for patient and staff safety
- Stay calm and relaxed
- Be firm but not ambitious
- Only attempt when all participants are ready as some cats have a express amount of time they will tolerate handling
- Close all doors and windows
- Allow the cat to get out its cage or carrier of its own volition if possible
- Watch carefully for alert signs (beginning to growl, swishing the tail) as unlike dogs, cats rarely assault without alert
- Do not allow an owner to restrain their ain fearful or aggressive cat as this may lead to the owner existence injured or fleck
- Scruffing the cat by the neck is one mode to control the true cat without hurting information technology
- Consider giving pain medication if the patient is painful or if pain is expected to be induced during a procedure
- Consider chemical restraint/sedation if the patient is overtly aggressive, nervous, or hard to handle as information technology may be safer for both the patient and the handler
- Always recall that your safety is of the utmost importance
Source: https://vmcli.com/continuing-education/proper-animal-handling-restraint/
Posted by: marshpabeggetur.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Are Some Similarities In Restraining Small And Large Animals"
Post a Comment